Introduction¶
DDI-Lifecycle is designed to document and manage data across the entire life cycle, from conceptualization to data publication and analysis and beyond. It encompasses all of DDI-Codebook (https://ddialliance.org/Specification/DDI-Codebook/2.5/) specification and extends it.
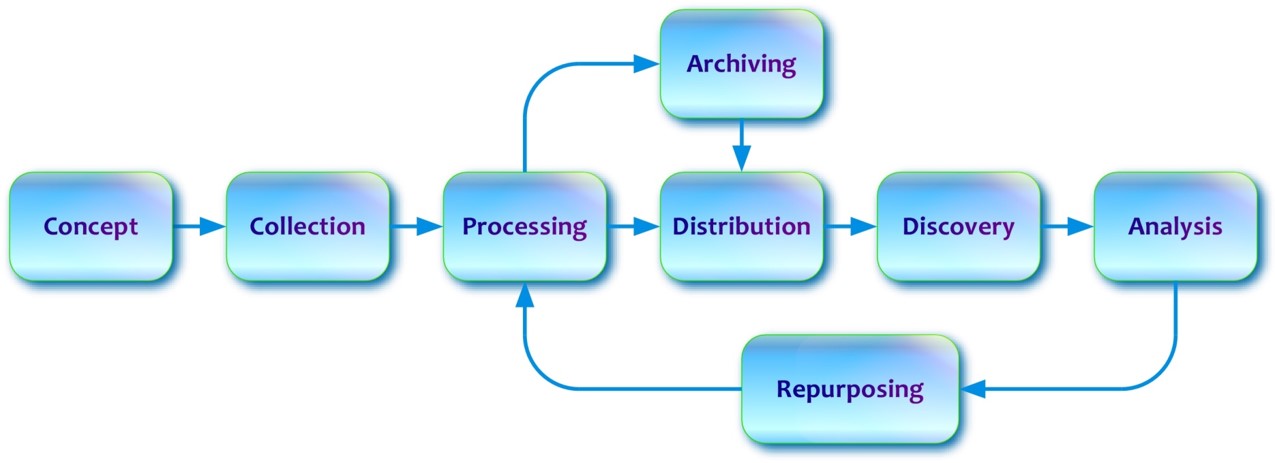
Figure 1 - DDI Lifecycle Model:
DDI-Lifecycle Coverage¶
Concept, Unit Type and Unit¶
DDi-Lifecycle mirrors ISO/IEC 11179. Concepts are a unit of knowledge created by a unique combination of characteristics, a Unit Type is a synonym of Object, which is a class or object of interest. The combination allows a single concept to be used between different Unit Types and hence Units.
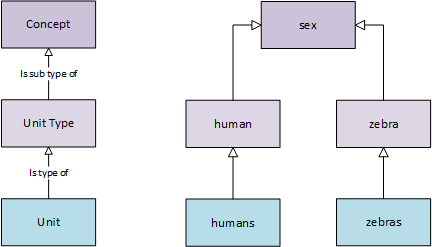
A Concept may have sub-concepts, and can be organised hierachically.
Universe and population¶
DDI-Lifecycle differentiates between a Universe and a population. A universe is a restriction on a Unit Type (e.g. live births) of humans, and a population is a universe bounded by time and geography. N.B. DDI-Lifecycle does not have an explicit population element, but allows it to be described.
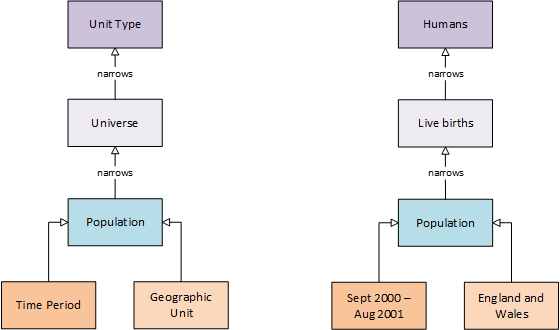
Schema Documentation: Universe
Concepts and other elements in DDI-Lifecycle¶
Concepts are a cornerstone of DDI-Lifecycle, nearly 50 elements have a relationship to it. These include (among others):
- Categories and ClassificationItems
- Conceptual Variables, Represented Variables and Variables
- Geographic Location and Geographic Structure Groups
- Measurement Items
- Questions (Items, Grids and Blocks)
- Quality Standards
- Sampling Information
- Universe and Unit Type (as described above)
Individuals, Organizations and Relations¶
DDI-Lifecycle supports complex relationships between individuals and organizations, both at a single and multiple time points. Individuals can be described using unique identifiers such as ORCID, as well as structures to support contact information, the periods for which an individual has a relationship with an organization, and the longevity of organisations. Descriptions, keywords and other affiliations are also supported.
Schema Documentation:
Data Capture¶
Data Collection Data Capture Flow Questions and Measures
Data Description and Metadata Management¶
Data Management and Production¶
Versioning, Provenance and Identification¶
Classification, GSIM and Nuechatel¶
A Study is composed of many elements, DDI-Lifecycle allows these to be captured and described in a consistent manner so that the data can be used independently of the producer.
- Study Unit
- is made up of information about who did what and information about its dissemination – it is designed to describe for instance a sweep or wave of a ‘study’
- Conceptual
- comprises those elements that define the ideas and concepts, the data that will be generated, the universe of interest and the geographical area of interest
- Data Collection
- describes how and why and in which way the data was collected, including methodology used, and any processing
- Data
- Logical Product – describes the data, the meaning of the data, the relationships between the different data items
- Physical Product – describes the structure and layout of the data, irrespective of the physical rendering of the data
- Physical Instance – describes the actual data, provides a place to cite and describe the coverage, where it is located and any issues relating to quality and statistical summaries
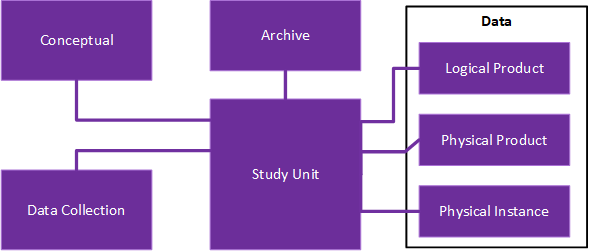
DDI Lifecycle Coverage:
Foundational Elements¶
Concept, UnitType, Universe SubUniverseClass
Category CodeList
ConceptualComponent
Individual Organization Relation
- Data Capture
- Data Description
- Survey Development
- Statistical Classification
- Administrative
- Comparison
- Grouping
- Schemes
Also, some other high level topics relating to implementation that were in the old User Guide